By Jim O’Neal
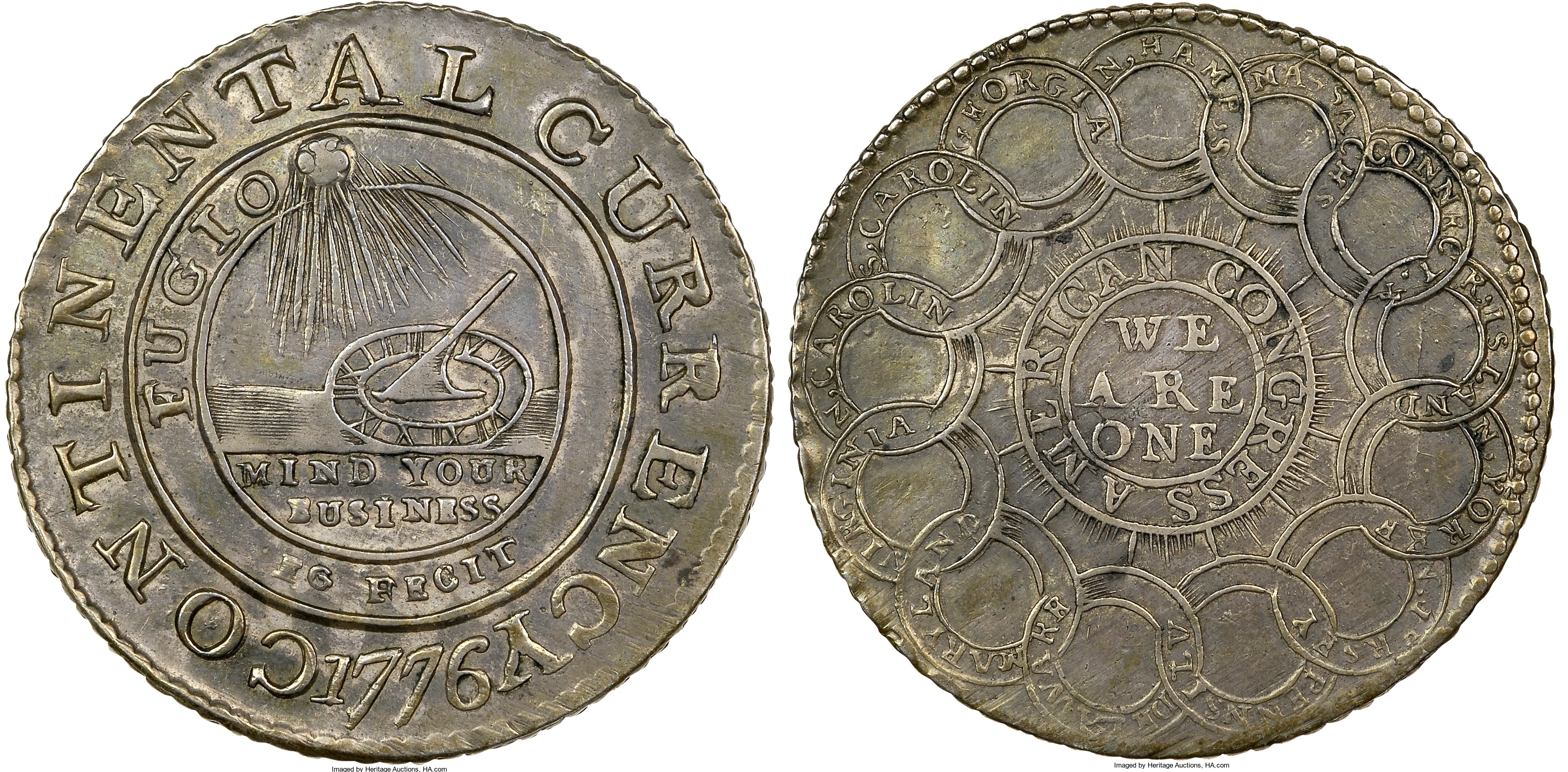
From Sept. 4 to Oct. 26, 1774, a group of delegates from every colony except Georgia met in Philadelphia in response to the British imposition of the Intolerable Acts. Although declaring independence was not the purpose of the meeting – sympathies ranged from loyalty to rebellion – they did pass 10 resolutions enumerating their rights and agreed to meet again if their grievances were not addressed by the Crown.
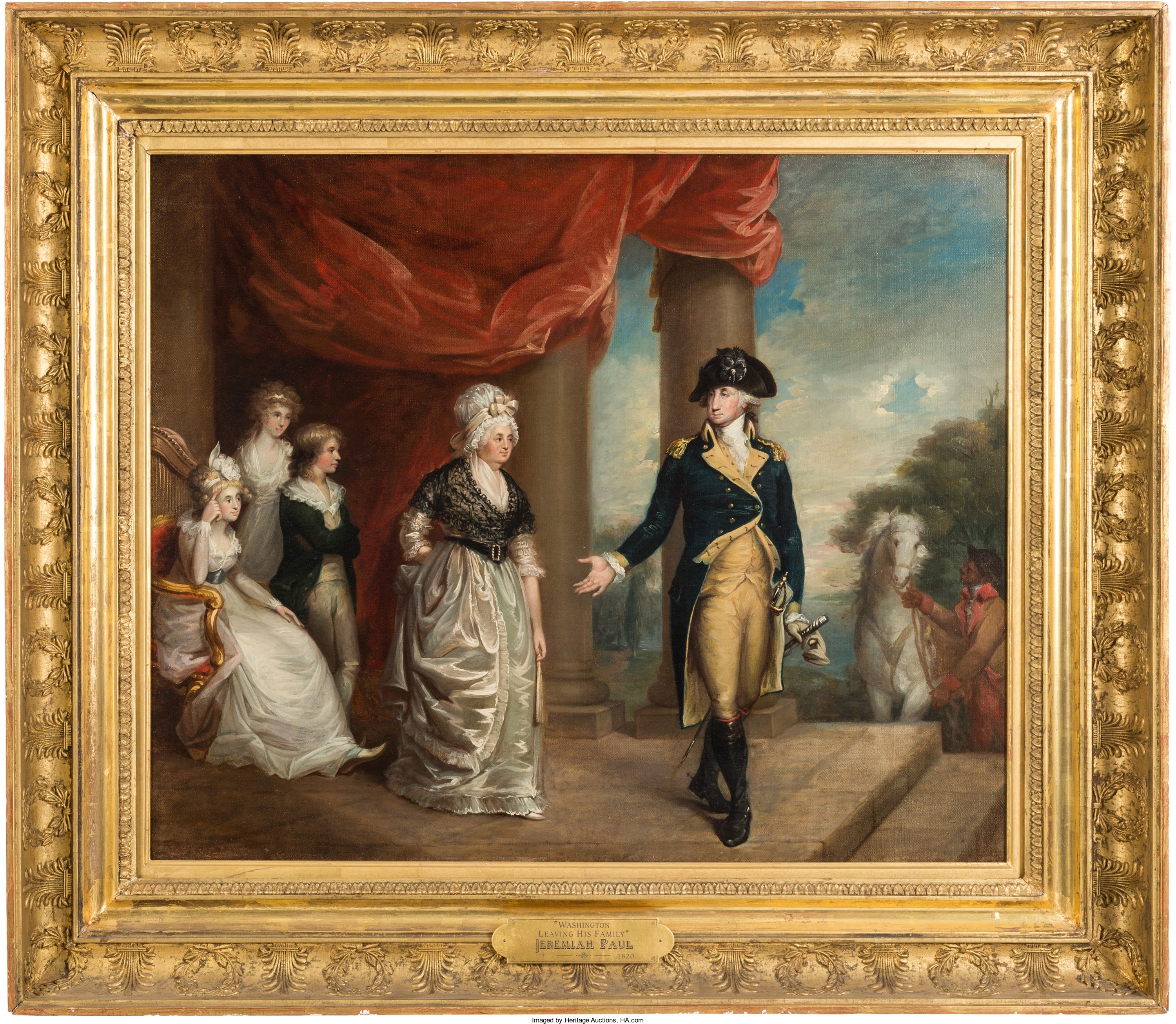
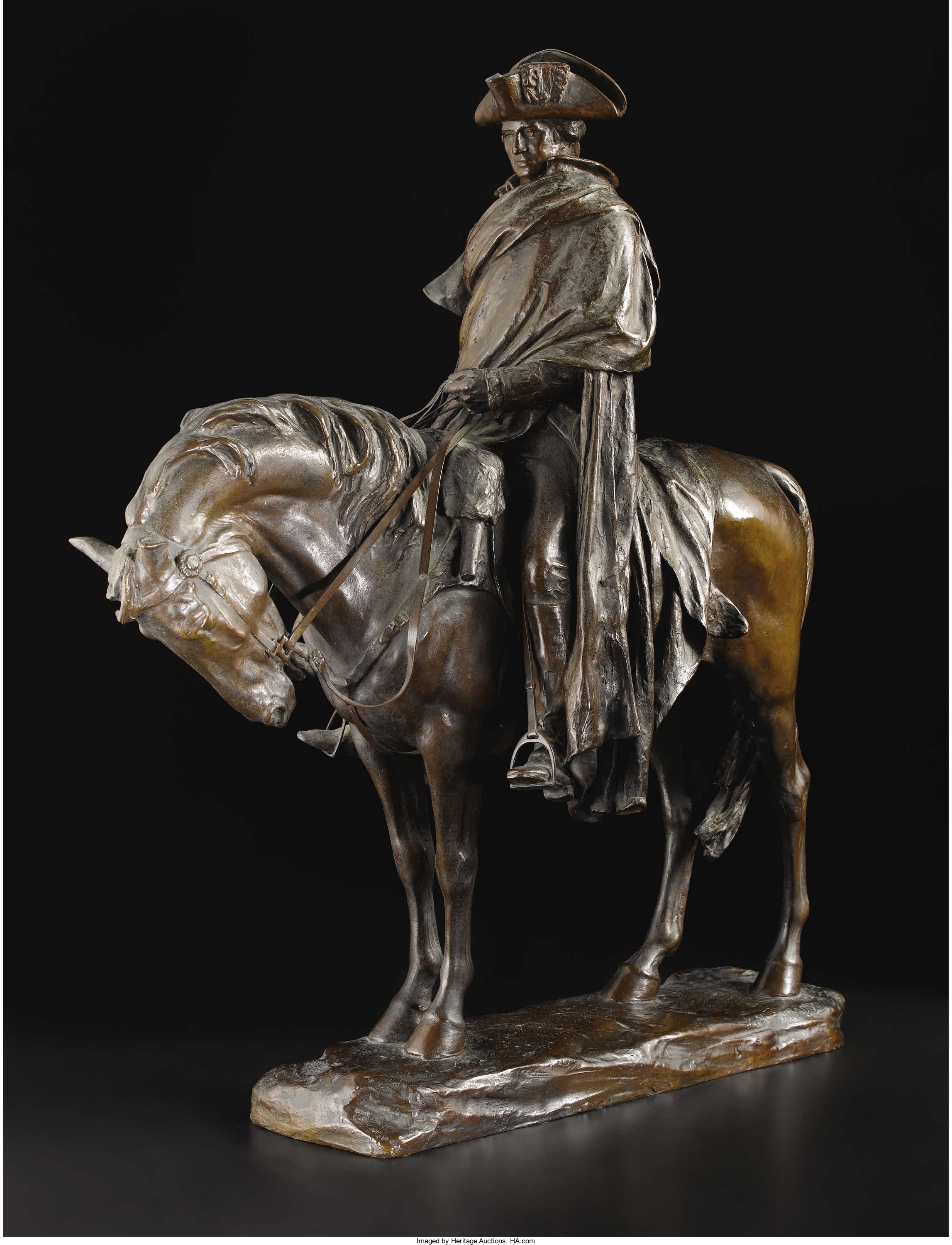
They met again in May 1775 and in June they appointed George Washington commander of a newly founded Continental Army. On July 4, 1776, the Congress issued a Declaration of Independence.
This upset King George III, who was an insecure man of average intelligence, but bewildered by the rash of constitutional arguments the Americans were asserting. He was the third of the Hanoverian Kings (his father had died and his grandfather still spoke with a deep German accent) and was firmly convinced the welfare of Great Britain was heavily reliant on the American Colonies.
The Colonies had become a major importer of British goods, surpassing even the West Indies, and his greatest nightmare was any interruption of this trade. “If we lose the American Colonies, we shall sink back into obscurity and be just a small, insignificant island once again.” He was adamant about not letting this occur.

By then, the population in America was 2.5 million (500,000 slaves, of which 200,000 were in Virginia), living in 13 Colonies and uniting for independence, despite the government being in total disarray. Some had colonial governments in place, but in colony after colony, revolutionary leaders had supplanted official British rule.
The Second Continental Congress convened in May 1775 in Philadelphia right after the Battles of Lexington and Concord and soon evolved into a national entity. After the formal Declaration of Independence, all that was left to do was defeat a vastly superior British Army, which was supremely confident its 5,000 soldiers could march the entire length, quashing any resistance as they went. We all know how this ended, but the tribulations of an underfunded, out-manned army are still inspiring.
It would be hard to overestimate the personal contributions and leadership that George Washington provided, and to call him “indispensable” is an understatement. Absent his presence, a very different outcome was highly likely. The “Father of Our Country” is one individual who will not be lost in the sands of history.
 Intelligent Collector blogger JIM O’NEAL is an avid collector and history buff. He is president and CEO of Frito-Lay International [retired] and earlier served as chairman and CEO of PepsiCo Restaurants International [KFC Pizza Hut and Taco Bell].
Intelligent Collector blogger JIM O’NEAL is an avid collector and history buff. He is president and CEO of Frito-Lay International [retired] and earlier served as chairman and CEO of PepsiCo Restaurants International [KFC Pizza Hut and Taco Bell].