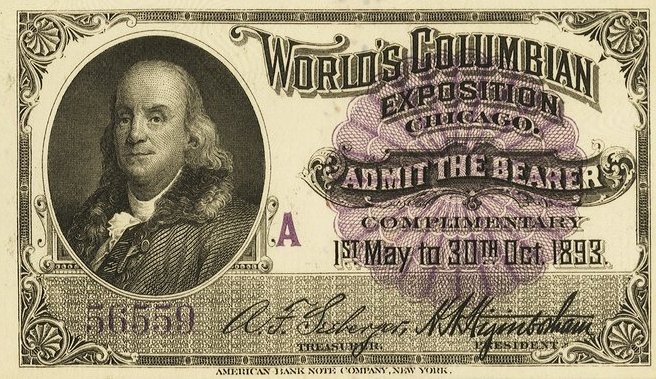
By Jim O’Neal
In 2003, bestselling author Erik Larson wrote The Devil in The White City, a non-fiction narrative of a serial killer who murdered up to 200 people using the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition (the Chicago World’s Fair) as a backdrop. Leonardo DiCaprio reportedly has the film rights and Martin Scorsese will direct.
There was a lot of competition for the fair between Chicago and New York City. NYC bolstered their bid when Cornelius Vanderbilt, William Waldorf Astor and J.P. Morgan pledged $15 million in support. But Chicago prevailed by matching the $15 million from Marshall Field, Philip Armour and Gustavus Swift (of meatpacking fame, who sold “Everything but the squeal,” a highly effective slogan highlighting how they used all animal parts to make other products and eliminate pollution).
However, what sealed the deal was a pledge by Lyman Gage, president of the powerful First National Bank of Chicago, to provide millions of dollars to help finance exhibitors. Gage would later serve as the 42nd Secretary of the Treasury under both William McKinley and Teddy Roosevelt.
Chicago was eager to host the event and demonstrate how much progress they had made after the disastrous Fire of 1871 involving Mrs. O’Leary’s cow. They painted so many stucco buildings white and had new electric lights illuminating so many streets that they earned the nickname “The White City.” They successfully conveyed the image of fresh, sanitary and new. There was also a major initiative called City Beautiful that included cleaning up trash in streets, empty lots and alleys.
A major mistake they made was denying William Frederick Cody (“Buffalo Bill”) permission to perform his famous Wild West Show. Ever the shrewd businessman, he simply set up shop outside the fairgrounds and siphoned off customers. However, the fair’s shaky finances received a big boost when Pittsburgh-based bridge maker George Ferris debuted his new invention – a 264-foot-tall Ferris Wheel. It could accommodate 2,160 people at a time and with a fare of 50 cents (double the cost of a fair ticket), it bailed out the fair and wiped out a big budget deficit.
The federal government also pitched in with the introduction of the country’s first postcards, a new commemorative stamp, and two new commemorative coins. One was a quarter featuring Queen Isabella – who financed the voyage of Columbus. It was the first time a U.S. coin honored a woman. The other was the 50-cent commemorative Columbus coin, both still popular with coin collectors today. The entire fair was an homage to Columbus, celebrating his voyage 400 years earlier, despite being one year late.
On July 12, American historian Frederick Jackson Turner skipped the Wild West Show and the docking of a replica from Norway of a Viking ship – just two of the hundreds of events that attracted up to 28 million spectators to the fair. Turner opted to put some finishing touches on his thesis before delivery at the Art Institute of Chicago that night.
More on his historic speech in my next post.
 Intelligent Collector blogger JIM O’NEAL is an avid collector and history buff. He is President and CEO of Frito-Lay International [retired] and earlier served as Chairman and CEO of PepsiCo Restaurants International [KFC Pizza Hut and Taco Bell].
Intelligent Collector blogger JIM O’NEAL is an avid collector and history buff. He is President and CEO of Frito-Lay International [retired] and earlier served as Chairman and CEO of PepsiCo Restaurants International [KFC Pizza Hut and Taco Bell].